Abstract
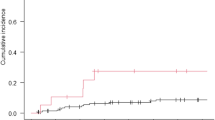
We investigate the differences in molecular signature and clinical outcomes between multiple lesion glioblastoma (GBM) and single focus GBM in the modern treatment era. Between August 2000 and May 2010, 161 patients with GBM were treated with modern radiotherapy techniques. Of this group, 33 were considered to have multiple lesion GBM (25 multifocal and 8 multicentric). Patterns of failure, time to progression and overall survival were compared based on whether the tumor was considered a single focus or multiple lesion GBM. Genomic groupings and methylation status were also investigated as a possible predictor of multifocality in a cohort of 41 patients with available tissue for analysis. There was no statistically significant difference in overall survival (p < 0.3) between the multiple lesion tumors (8.2 months) and single focus GBM (11 months). Progression free survival was superior in the single focus tumors (7.1 months) as compared to multi-focal (5.6 months, p = 0.02). For patients with single focus, multifocal and multicentric GBM, 81, 76 and 88 % of treatment failures occurred in the 60 Gy volume (p < 0.5), while 54, 72, and 38 % of treatment failures occurred in the 46 Gy volume (p < 0.4). Out of field failures were rare in both single focus and multiple foci GBM (7 vs 3 %). Genomic groupings and methylation status were not found to predict for multifocality. Patterns of failure, survival and genomic signatures for multiple lesion GBM do not appreciably differ when compared to single focus tumors.

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Showalter TN, Andrel J, Andrews DW, Curran WJ Jr, Daskalakis C, Werner-Wasik M (2007) Multifocal glioblastoma multiforme: prognostic factors and patterns of progression. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:820–824
Thomas RP, Xu LW, Lober RM, Li G, Nagpal S (2013) The incidence and significance of multiple lesions in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 112:91–97
Patil CG, Yi A, Elramsisy A, Hu J, Mukherjee D, Irvin DK, Yu JS, Bannykh SI, Black KL, Nuno M (2012) Prognosis of patients with multifocal glioblastoma: a case-control study. J Neurosurg 117:705–711
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963–1972
Liu W, Lindberg J, Sui G, Luo J, Egevad L, Li T, Xie C, Wan M, Kim ST, Wang Z, Turner AR, Zhang Z, Feng J, Yan Y, Sun J, Bova GS, Ewing CM, Yan G, Gielzak M, Cramer SD, Vessella RL, Zheng SL, Gronberg H, Isaacs WB, Xu J (2012) Identification of novel CHD1-associated collaborative alterations of genomic structure and functional assessment of CHD1 in prostate cancer. Oncogene 31:3939–3948
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP, Alexe G, Lawrence M, O’Kelly M, Tamayo P, Weir BA, Gabriel S, Winckler W, Gupta S, Jakkula L, Feiler HS, Hodgson JG, James CD, Sarkaria JN, Brennan C, Kahn A, Spellman PT, Wilson RK, Speed TP, Gray JW, Meyerson M, Getz G, Perou CM, Hayes DN (2010) Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 17:98–110
Du P, Kibbe WA, Lin SM (2008) Lumi: a pipeline for processing Illumina microarray. Bioinformatics 24:1547–1548
Kim JW, Kim ST, Turner AR, Young T, Smith S, Liu W, Lindberg J, Egevad L, Gronberg H, Isaacs WB, Xu J (2012) Identification of new differentially methylated genes that have potential functional consequences in prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 7:e48455
Bady P, Sciuscio D, Diserens AC, Bloch J, van den Bent MJ, Marosi C, Dietrich PY, Weller M, Mariani L, Heppner FL, McDonald DR, Lacombe D, Stupp R, Delorenzi M, Hegi ME (2012) MGMT methylation analysis of glioblastoma on the Infinium methylation BeadChip identifies two distinct CpG regions associated with gene silencing and outcome, yielding a prediction model for comparisons across datasets, tumor grades, and CIMP-status. Acta Neuropathol 124:547–560
Noushmehr H, Weisenberger DJ, Diefes K, Phillips HS, Pujara K, Berman BP, Pan F, Pelloski CE, Sulman EP, Bhat KP, Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Hayes DN, Perou CM, Schmidt HK, Ding L, Wilson RK, Van Den Berg D, Shen H, Bengtsson H, Neuvial P, Cope LM, Buckley J, Herman JG, Baylin SB, Laird PW, Aldape K (2010) Identification of a CpG island methylator phenotype that defines a distinct subgroup of glioma. Cancer Cell 17:510–522
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, Williams PM, Modrusan Z, Feuerstein BG, Aldape K (2006) Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 9:157–173
Grossman SA, Ye X, Chamberlain M, Mikkelsen T, Batchelor T, Desideri S, Piantadosi S, Fisher J, Fine HA (2009) Talampanel with standard radiation and temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 27:4155–4161
Paulsson AK, McMullen KP, Peiffer AM, Hinson WH, Kearns WT, Johnson AJ, Lesser GJ, Ellis TL, Tatter SB, Debinski W, Shaw EG, Chan MD (2014) Limited margins using modern radiotherapy techniques does not increase marginal failure rate of glioblastoma. Am J Clin Oncol 37:177–181
Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Franceschi E, Sotti G, Frezza G, Amista P, Morandi L, Spagnolli F, Ermani M (2009) Recurrence pattern after temozolomide concomitant with and adjuvant to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma: correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. J Clin Oncol 27:1275–1279
Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, McLendon R, Rasheed BA, Yuan W, Kos I, Batinic-Haberle I, Jones S, Riggins GJ, Friedman H, Friedman A, Reardon D, Herndon J, Kinzler KW, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B, Bigner DD (2009) IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N Engl J Med 360:765–773
Dobelbower MC, Burnett Iii OL, Nordal RA, Nabors LB, Markert JM, Hyatt MD, Fiveash JB (2011) Patterns of failure for glioblastoma multiforme following concurrent radiation and temozolomide. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 55:77–81
Simpson JR, Horton J, Scott C, Curran WJ, Rubin P, Fischbach J, Isaacson S, Rotman M, Asbell SO, Nelson JS et al (1993) Influence of location and extent of surgical resection on survival of patients with glioblastoma multiforme: results of three consecutive radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) clinical trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 26:239–244
Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen HJ (2006) Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 7:392–401
Hassaneen W, Levine NB, Suki D, Salaskar AL, de Moura Lima A, McCutcheon IE, Prabhu SS, Lang FF, DeMonte F, Rao G, Weinberg JS, Wildrick DM, Aldape KD, Sawaya R (2011) Multiple craniotomies in the management of multifocal and multicentric glioblastoma: clinical article. J Neurosurg 114:576–584
Acknowledgements
The investigators responsible for this manuscript would like to sincerely thank Marlene Pratto and the Pratto Fund for Brain Tumor Research for the generous gift which helped to fund this research. We would like to thank Dr. Thomas L. Ellis, who contributed significantly to this work until his untimely death in 2012. We would also like to thank our patients as they are the inspiration behind our work. This work has previously been presented at the ASTRO 2012 National Meeting in Boston, MA.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
Pratto Fund for Brain Tumor Research; Dalton McMichael Fund in Cancer Research (to A.M.P); Comprehensive Cancer Center of Wake Forest University supported by the National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant [P30CA012197].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paulsson, A.K., Holmes, J.A., Peiffer, A.M. et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes and genomic characteristics of single focus and multifocal glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 119, 429–435 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1515-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1515-1